
ELBOW Fracture
Elbow injuries can become painful and may require immediate attention. If you suspect your child has a broken elbow, visit one of our Fracture Care Clinics in Dallas, Arlington, Frisco, or McKinney, Texas and our pediatric orthopedic physicians will see you right away.
Fractured elbows appear among the most common injuries we see in children.
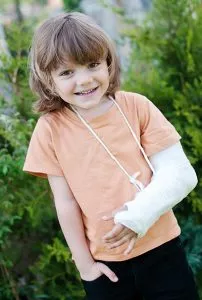
Broken Elbow
Children are active and can fall onto their arms, thereby leading to a fracture. Whether your child is a toddler crawling around or an active little kid running around, there’s a high probability that he or she will fall at home or on the playground. If the child falls fast and under high pressure, the bone around the elbow may end up breaking. For example, we see a lot of broken elbows in children and these injuries account for about 10% of fractures in children.
At Medical City Children’s Orthopedic and Spine Specialists, our physical therapists, pain management specialists, and orthopedic specialists work together to provide customized treatment and recovery plans for children. Then we work with patients for as long as required to ensure that function gets restored and pain gets reduced or eliminated.
Anatomy of the Elbow
The elbow joint comprises three bones that allow the elbow to bend and straighten. These bones also allow the forearm to rotate. They include:
Humerus
This bone is found in the upper arm and runs from the shoulder to the elbow.
Radius
This forearm bone runs from the elbow to the wrist. It is found on the thumb side of the forearm. The bone rotates when the wrist rotates.
Ulna
This forearm bone runs from the elbow to the wrist. It is found on the pinky side of the forearm. Also, the ulna acts as the hinge in the elbow and allows the elbow to bend and straighten.
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
What constitutes a broken elbow in children, and what are the common causes?
A broken elbow in children, also known as an elbow fracture, occurs when a break or crack in one or more of the bones that make up the elbow joint. The elbow comprises the humerus (upper arm bone), ulna, and radius (bones of the forearm). Common causes of a broken elbow in children include falls onto an outstretched hand, direct blows to the elbow, sports-related injuries, or trauma from accidents. The severity and type of fracture can vary, ranging from a simple crack to a more complex break involving multiple bones.
How do doctors diagnose and treat a child with a broken elbow?
Diagnosis of a broken elbow in a child involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional, often including a physical examination and imaging studies like X-rays or sometimes CT scans to visualize the extent and location of the fracture. Treatment may range from simple immobilization with a cast or splint for less severe fractures to more complex interventions like surgery for severe or displaced fractures. Your doctor will align the bones properly and ensure proper healing to restore function and prevent long-term complications.
What is the recovery process for a child with a broken elbow, and are there potential long-term effects?
The recovery process for a broken elbow in a child can vary based on the type and severity of the fracture. It typically involves a period of immobilization, followed by rehabilitation, which may include physical therapy to regain strength, flexibility, and mobility of the elbow joint. The duration of recovery can range from several weeks to a few months, depending on the complexity of the fracture.
Potential long-term effects may include stiffness, decreased range of motion, or in some cases, ongoing pain or weakness. However, with appropriate medical care, rehabilitation, and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan, many children with a broken elbow can achieve a good recovery with minimal long-term effects. Regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals are essential to monitor progress and address any concerns during the healing process.
Our Board-Certified Physicians Treat Growth Plates in Growing Bones.
“Since elbow fractures are often seen around the growth plate area, an injury to the growth plate can occur. Our pediatric orthopedic physicians have the expertise to treat growth plate injuries and we watch the child over time to ensure their growth plate has not been injured.” Shyam Kishan, MD
What Are Broken Elbows?
A broken (or fractured) elbow refers to a break at or close to the elbow joint. The break occurs in one or more of the three bones that make up the elbow.
A broken elbow usually occurs in children as a result of an impact injury. As such, we treat this injury by splinting or casting the affected area for about 1 month.
Symptoms of a Broken Elbow
The child may have a broken or sprained elbow if the parent notices the following:
- Swelling of the elbow or in areas above or below the elbow
- Deformed elbows (or deformity in the areas above or below the elbow)
- Discoloration, redness, or bruising of the elbow
- ‘Tight sensation’ in the forearm or areas of the elbow
- A cut on the elbow after an injury
- Numbness or a cool sensation in the forearm, hand, or fingers
- Inability or difficulty moving the elbow via its complete range of motion
Causes of Broken Elbows in Children
Broken elbows in children usually occur because of the following:
- The child falling on his or her elbow
- A fall on an outstretched arm, and
- A direct blow to the elbow
Children are always involved in activities that make them prone to injuring their elbows. Also, we see most of the elbow injuries occurring on the playground when the child falls after losing their grip on the monkey bars. If a toddler falls from a lower height, he or she can also sustain an elbow fracture.
Fractured elbows also occur in sports, like football or gymnastics, or recreational activities like bicycling or skateboarding. Consequently, children can avoid the risk of breaking an elbow by wearing protective elbow guards and pads.
Types of Elbow Fracture
The common types of fractured elbows include:
Supracondylar humerus fracture
This is the most common type of elbow fracture. It occurs through the growth plate of the humerus (found above the elbow joint). This type of elbow fracture is usually caused by a fall onto an outstretched arm. It is usually found in children that are 5 to 7 years old.
Condylar fracture
This fracture also occurs just above the elbow joint. It occurs when a child breaks one side of the elbow joint.
Radial neck fracture
Doctors treat this type of elbow fracture based on the angle at which the fracture occurred. The treatment comprises casting, manipulation, or placing pins across the fracture.
Radial head subluxation
Although this does not involve a broken bone, young children often have this common injury. When this type of injury occurs, the elbow joint will slide out of its position. Doctors will return the elbow joint to the correct position through manipulation or surgical treatment.
Olecranon fracture
This type of elbow fracture injures the prominent bone located at the back of the elbow. Doctors know that differentiating injuries to this bone from the normal appearance of growth plates is problematic. An X-ray of both elbows will assist in the diagnosis.
Diagnosis
To diagnose a broken elbow, the doctor will check the skin around the elbow, forearm, and wrist and will also touch these areas to discover the area that hurts. In addition, the doctor may also try to move the joints. And then test the nerves and circulation to the hand. In most cases, X-rays are needed to diagnose a broken elbow. Since forearm fractures are associated with elbow fractures, the doctor may request X-rays of the forearm as well.
In young children, the bones in the elbow are made up of cartilage and are also soft; they do not reflect in the X-ray. In this case, the doctor may order X-rays of the other elbow to compare them. The doctor may also ask for an MRI ultrasound or an arthrogram, whereby dye gets injected into the joint. This will help the doctor to see the surfaces of the bones and the elbow joint.
Treatment
If a broken elbow heals in the wrong position, the elbow may become permanently distorted and may not have a full range of motion. Therefore, as soon as a parent finds that their child sustained a broken elbow, the child should be taken to a pediatric orthopedist for treatment as soon as possible.
The specific treatment administered for a broken elbow depends on the following factors:
- The child’s age
- The location of the fracture
- Damage to the nerves and blood vessels
- The severity of the displacement
Non-surgical treatment
Parents need to stabilize their child’s elbow fracture as soon as possible because they can normally heal without applying a cast or splint. So, the next step for the parent is to have a doctor reposition the bones before a splint or cast is applied. If the fracture is stable without any displacement, the doctor may apply a splint or cast to an active child to ensure that the bones remain in proper alignment while healing. Unlike casts, splints provide less support. However, it is easy to adjust them to accommodate swelling. When X-rays confirm an elbow fracture, splints work to stabilize the joint until the swelling goes down and then cast the elbow. Also, the doctor may also schedule additional X-rays to ensure the bones remain in the right place while they heal.
Doctors often use casts to treat elbow fractures. More commonly, we will splint the joint for a week while the swelling subsides, and then put a cast on the child’s arm.
Surgical treatment
if the bone fragments appear displaced, surgery becomes necessary to make sure the fracture heals completely. The surgical treatments used for broken elbows include:
- Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning
This surgical procedure joins displaced fragments of the bone during closed reduction and becomes held in place with metal pins. During the procedure, the surgeon will insert the pins through the skin, into the bone, and across the fracture. Accordingly, the affected area gets protected for the first week with a splint. When healing has begun, a few weeks after surgery, the surgeon will remove the pins and the cast.
- Open reduction and internal fixation
Fractures that do not respond to alignment during a closed reduction and those that cause nerve or vascular damage require a surgical approach.
Recovery
 Irrespective of the treatment method used, the doctor will place the arm in a cast or splint for about 3 to 6 weeks, depending on the type of fracture. When the fracture has healed, the doctor may recommend some types of exercise to improve the joint’s range of motion. After treatment, the range of motion of the elbow usually returns to normal or may have a mild limitation.
Irrespective of the treatment method used, the doctor will place the arm in a cast or splint for about 3 to 6 weeks, depending on the type of fracture. When the fracture has healed, the doctor may recommend some types of exercise to improve the joint’s range of motion. After treatment, the range of motion of the elbow usually returns to normal or may have a mild limitation.
Long-Term Complications of a Broken Elbow
Since elbow fractures occur around the growth plate, the growth plate can get injured; thereby, leading to the early closure of the growth plate. Although rare, the best way to know if the growth plate got injured is for the orthopedic surgeon to monitor the growth of the child’s limb.
Other long-term complications of a broken elbow include:
- Damage to nerves and blood vessels around the elbow
- Restriction of the movement of the elbow joint, and
- Infection of the pins placed into the elbow
Here at Medical City Children’s Orthopedic and Spine Specialists, our doctors will follow your child to monitor the condition of the injury until it heals completely. We may also ask for a follow-up to make sure that growth and movement around the elbow return to normal.
Schedule a Free Consultation for Your Child’s Elbow Care
Medical City Children’s Orthopedic and Spine Specialists with offices in Arlington, Dallas, Flower Mound, Frisco, and McKinney, TX is a board-certified, fellowship-trained orthopedic group that uses both surgical and non-surgical techniques to treat spine diseases, sports injuries, musculoskeletal trauma, and degenerative diseases. As such, our specialists provide cutting-edge and comprehensive care in diagnosing and treating broken elbows. Also, we use the latest state-of-the-art treatment methods to return children, adolescents, and adults to their active lifestyles.
Finally, speak to one of our compassionate and expert orthopedic surgeons today to learn more about your child’s broken elbow and the specific treatment procedure to reduce and eliminate pain.
____________________
Footnote:
At Medical City Children’s Orthopedic and Spine Specialists, we have pediatric physicians with the expertise to treat elbow fractures and injuries to the growth plates. Our board-certified physicians specialize in the treatment of children and adolescents and can give your child the care and attention they deserve to continue their healthy active life.
Call 214-556-0590 for an appointment.
Comprehensive services for children from birth through adolescence at five convenient locations: Arlington, Dallas, Flower Mound, Frisco and McKinney.
