
EPIPHYSEAL BRACKET FOOT
Epiphyseal bracket Foot or bracket epiphysis is an uncommon disorder of bone growth in the hands or feet. This condition produces bone cells that extend longitudinally along the mid-section of a bone. Although rare, longitudinal epiphyseal bracket most commonly manifests in the hands as clinodactyly and in the feet as Hallux Varus
If your child needs surgery or casting, our Fracture Care Clinic opens every day and you do not need an appointment. Surgery rooms get scheduled every morning, so your child receives the care and attention they need right away.
Epiphyseal Bracket Foot
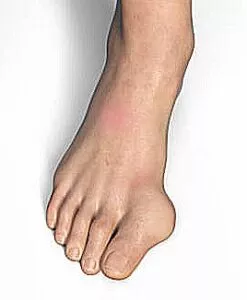 Longitudinal epiphysis or bracket epiphysis is a rare growth defect. It originates from the body producing new bone in the hands or feet. When found in the feet, doctors refer to the extra bone as Hallux Varus. Hallux valgus (HV), also known as a bunion, is one of the most common forefoot deformities. Surgeons use Angular osteotomy to treat longitudinal epiphyseal brackets, and some doctors recommend this treatment occur as soon as possible.
Longitudinal epiphysis or bracket epiphysis is a rare growth defect. It originates from the body producing new bone in the hands or feet. When found in the feet, doctors refer to the extra bone as Hallux Varus. Hallux valgus (HV), also known as a bunion, is one of the most common forefoot deformities. Surgeons use Angular osteotomy to treat longitudinal epiphyseal brackets, and some doctors recommend this treatment occur as soon as possible.
A rare ossification condition of the tubular bones of the hands and feet called longitudinal epiphyseal bracket is caused by an abnormally continuous physical tissue along the diaphysis. The disease affects fingers and toes. Polydactyly is frequently linked to the “D” shaped metatarsal. Less frequently, a longitudinal epiphyseal bracket can develop in the tibia. Additionally, it grows and becomes visible on both sides of a bone. In this case, it is referred to as a duplicated longitudinal epiphysis or “kissing bracket.” The following terms all refer to this extra bone growth:
- Bracket epiphysis
- Delta phalanx
- Delta bone
- Longitudinal bracketed diaphysis
- Congenital angular deformity
Epiphyseal Bracket Foot Causes
If your child’s big toe is hallux varus, it simply indicates that it angles unusually away from your second toe. The following provide other causes for the disease.
- A congenital abnormality
- A tendon issue
- Rupture of the ligament at the metatarsophalangeal (The problem frequently arises as a side effect following bunion surgery or results from trauma)
- Too large or too short abductor hallucis tendon.
- A Trauma
The most typical symptom is discomfort brought on by the toe rubbing against a shoe’s inside. Additionally, it may increase the likelihood of developing an ingrown toenail.
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
What constitutes epiphyseal bracket foot in children, and how does it affect them?
Epiphyseal bracket foot, a congenital condition where the tibia bows inwards, creates a bracket-like shape. This condition typically appears at birth and can affect one or both legs. Doctors say the condition stems from abnormal development at the growth plate (epiphysis) of the tibia. The bowing can vary in severity and may affect a child’s ability to walk and engage in physical activities.
What symptoms and signs of identify epiphyseal bracket foot in children?
Children with epiphyseal bracket foot may have visibly bowed or bracket-shaped legs, especially around the lower part of the shin. Doctors may observe the condition at birth or during early childhood. Other signs may include difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg, an abnormal gait, or an altered walking pattern. If left untreated, the condition can potentially cause problems with mobility and affect the child’s quality of life.
How do doctors diagnose and treat epiphyseal bracket foot in children?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and imaging studies, such as X-rays, to assess the alignment and structure of the tibia and determine the severity of the bowing. Treatment may vary depending on the child’s age, the severity of the condition, and its impact on mobility. Early intervention is key to managing the condition effectively.
Treatment may involve a combination of non-surgical interventions, such as bracing or orthotics, to help support and straighten the leg. In more severe cases, doctors will consider surgical interventions like guided growth techniques or osteotomy (surgical bone cutting and realignment) to correct the alignment of the tibia.
Epiphyseal bracket foot, also known as congenital anteromedial bowing of the tibia (CABT), is a rare condition where the tibia (shinbone) is bowed or bent inward, resembling a bracket shape. We Treat this condition
Epiphyseal Bracket Foot Symptoms
The biggest symptom of a hallux varus deformity is a large toe that drifts. In addition to these signs of hallux varus:
- Chronic soreness.
- Trouble walking or standing.
- Trouble wearing close-toed shoes.
- Foot weakness.
- Ingrown toenails.
- Limited range of motion.
- Foot and ankle discomfort and swelling (caused by pressure on the toe).
Wearing shoes that squeeze your child’s toes together might make Hallux varus symptoms worse. Joint discomfort is not brought on by the illness. In addition, the majority of the pain that comes with hallux varus comes from friction between the toe and improperly fitted shoes.
Diagnosing Hallux Varus
Clinical examination and X-rays will show the deformity, but identifying the underlying reason will typically become identified by a thorough medical history from a qualified foot and ankle specialist.
Epiphyseal Bracket Foot Treatment
The kind of treatment your doctor will recommend depends on the cause. For instance, if a youngster possesses the disease, the doctor may advise lengthening the abductor hallucis tendon using a splint, physical therapy, or special shoes. In contrast, if non-surgical therapy fails, doctors will consider surgery. Following bunion surgery, other treatments may become necessary if the problem worsens. Generally speaking, the earlier the patient seeks help, the easier the procedure to correct the problem. Only surgery for severe hallux valgus, which makes walking painful, can provide a patient with long-term pain relief. Only physical therapy exercises and a splint can stop the illness from progressing in older patients. In this instance, the only choice for managing hallux valgus discomfort and avoiding problems in the metatarsophalangeal joint is surgically correcting the bunions.
Non-Surgical and Surgical Treatments for Epiphyseal Bracket Foot
The Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists provides a variety of hallux valgus non-surgery and surgery techniques. The following outline some of those treatments:
- To enable the straightening of the big toe, the tendons and joint capsule get corrected using a soft tissue treatment.
- The toes will often straighten again after a treatment on the big toe bone, which becomes repositioning by a procedure called an osteotomy.
- The Hallux valgus splint helps correct the crooked toe. The orthopedist at Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists will use conservative treatments to treat hallux valgus when found in its early stages.
- Doctors recommend insoles designed to support the front arch and stop the progression of splayfoot.
- Doctors recommend flat heels for hallux valgus footwear. Also, the toes maintain lots of flexibility due to the shoes’ large forefoot width.
- Exercises for the hallux valgus and barefoot walking can help the development of the deformity in its early phases.
- In order to effectively cure Hallux valgus, the pressure points on the foot must undergo regular skin care.
- Special Hallux valgus shoes that give the bunion more leeway can minimize friction, which in turn lowers swelling, inflammation, and discomfort associated with the condition.
- Insoles can support a splayfoot condition by raising the front arch, which causes the forefoot to narrow once again. This lessens friction-related discomfort to the bunion within the shoe, which can also lessen hallux valgus swelling.
Conclusion
Finally, contact Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists with offices in Arlington, Dallas, Flower Mound, Frisco, and McKinney, TX invites parents to speak with one of our specialists if your child has epiphyseal bracket. To make an appointment, phone us or reach out to us online.
Call 214-556-0590 to make an appointment.
Comprehensive services for children from birth through adolescence at five convenient locations: Arlington, Dallas, Flower Mound, Frisco and McKinney.
