
FOOT FRACTURE
A broken foot is an injury to at least one of 26 bones. Children usually break a bone in their feet from playing with other children. The seriousness of a broken foot varies from tiny cracks to compound fractures that break the skin.
If your child needs surgery or casting, our Fracture Care Clinic opens every day and you do not need an appointment. Surgery rooms get scheduled every morning, so your child receives the care and attention they need right away.
Foot Fracture
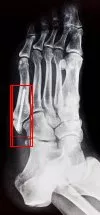
Repaired with a Screw
A complex bodily part, the foot carries out a number of special functions. Its 26 bones cooperate to support the entire body weight, keep your child upright, and let your child move quickly during activities like running and leaping. The forefoot, midfoot, and hindfoot are the foot’s three main structural components. The forefoot, which is the long front portion of the foot, has 19 bones total, including phalanges and metatarsals. The navicular, cuboid, and cuneiforms make up the midfoot’s five bones. The talus, which links to the ankle, and the calcaneus, which forms the heel, are the only two bones in the hindfoot.
A foot fracture happens when the foot sustains damage from an accident. Any of the foot’s bones might break, resulting in a foot fracture (tarsus, metatarsals, and phalanges). Direct trauma or an excessive load on the bone might cause damage. A fractured foot can range in severity. Fractures can be anything from minor bony fissures to skin-piercing breaks. If the break is significant, your child could need surgical implants to stabilize the position of the bones while he or she heals.
Two Major Foot Fracture Categories
There are two main categories of foot fractures: stress fractures brought on by excessive usage and complete foot fractures brought on by abrupt impact. There are significant variances, even if the degree of pain your child could feel from any type of foot injury may seem identical.
Stress fracture of the foot
One or more bones in the foot might break due to repetitive stress over time, leading to stress fractures.
Full Foot Fracture
There are two types of total foot fractures, both of which are usually the result of a one-time trauma such as a car accident or dropping a heavy object on the foot. Simple or complex fractures of the whole foot are also possible. Simple fractures, also known as closed fractures, do not harm the skin or tissue around them. Open fractures, also known as compound fractures, harm the skin and surrounding tissue. Since the break is typically significant enough to pierce skin and tissue, open-foot fractures are typically more dangerous than closed-foot fractures. Due to the exposed incision and injury to the soft tissue of the foot, an open fracture is also more prone to infection.
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
What constitutes a foot fracture in children, and how does it happen?
A foot fracture in children involves a break or crack in one or more of the bones in the foot. These fractures can occur due to various reasons, including falls, sports injuries, accidents, or trauma to the foot. The severity and location of the fracture can vary, from minor hairline cracks to more significant breaks that affect mobility and function.
How is a foot fracture in a child diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional, including assessing the affected foot’s appearance, tenderness, swelling, and range of motion. The doctor may order X-rays and sometimes other imaging studies to evaluate the location and extent of the fracture. Treatment varies depending on the severity and type of fracture. Doctors will treat minor fractures with rest, ice, elevation, and possibly a cast or splint. More severe fractures may require realignment (reduction) of the bones and immobilization with a cast or, in some cases, surgery to align and stabilize the bones using pins, screws, or plates.
Following treatment and rehabilitation, the doctor may recommend physical therapy to aid in recovery, regain strength, and restore function and mobility.
What is the recovery time and long-term prognosis for a child with a foot fracture?
Recovery time for a foot fracture in children varies based on the severity and type of fracture. Minor fractures may heal in a few weeks, while more complex fractures may take several weeks to months to heal. Full recovery, including returning to normal activities, may take several months to a year, and rehabilitation plays a vital role in this process. The long-term prognosis is generally good, especially with proper treatment and follow-up care. Children typically regain full function and mobility of the foot after proper healing and rehabilitation.
The doctors at Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists, are experts in treating foot fractures. To ensure your child’s bones heal properly, call us for an appointment
Causes of a Broken Foot
An automobile accident, tripping or falling awkwardly on your child’s foot, impact from a large object, such as dumping something heavy on your child’s foot, or even tension on the foot from overuse are some of the typical reasons for a fractured foot. Small fractures can develop over time as a result of repetitive efforts, such as long-distance jogging. The strains or direct hits from high-impact sports, as well as incorrect technique or equipment use, are risk factors for fractured feet or ankles. A rapid increase in exercise might also raise your child’s chance of developing a stress fracture. A medical condition like osteoporosis might increase your child’s chance of suffering damage to the bones in his or her foot.
Injuries to the Foot in Athletes
Due to a propensity to misdiagnose stress fractures as strains or sprains, athletes frequently experience stress fractures that get worse over time. Since a specific action does not cause a stress fracture, diagnosing one can be difficult for both doctors and patients. The most common causes of this type of foot injury are overuse and repetitive stress from activities such as running and jumping. Impact frequency, impact length, and impact severity are the three variables that affect the chance of getting a stress fracture in a foot.
The repetitive impacts from motions like running or jumping are related to all three causes. For instance, a hurdler would cause high-intensity strikes on the foot. A long-distance runner would produce effects that lasted for a very long time. A level of danger is there in both activities for athletes. Consult a doctor right away if you believe your child has a stress fracture or a complete foot fracture for a precise diagnosis, course of treatment, and rehabilitation schedule.
Symptoms
From bruises to excruciating agony, foot fracture symptoms might vary. If your child has one or more of the following typical foot fracture symptoms, see the following list and contact a doctor right away:
- Increasing foot discomfort as your child steps on it,
- Foot discomfort that gradually becomes worse over time,
- Swelling on the outside of the ankle
- The foot or ankle feels delicate to the touch.
- In certain instances, the ankle or foot displays indications of bruising.
Determining the Cause of Foot and Ankle Fractures
Parents should visit an orthopedic expert to get a diagnosis of a foot and ankle fracture so they can identify the extent of the damage and the best course of action. It is conceivable that imaging examinations, such as:
- Musculoskeletal ultrasound
- MRI
- CT scans
- Weight-bearing CT scan
What can I Expect from my Surgery?
Your anesthesiologist will discuss the type of anesthetic to use and the procedure, so your child won’t feel anything. You will have the chance to voice any queries or worries. Once safely anesthetized, an incision is made in the skin to break the leg bone. The bone is repositioned and fixed, usually with metal implants. Once the bone is repaired, the surgeon sutures the incision and returns to the room. Different leg fracture surgeries have specific techniques such as:
Heel Bone Surgery (Calcaneus)
Disruption of the joint between the heel bone and ankle bone is frequently a complication of a heel fracture (talus). Surgery is necessary to straighten the joint surface and restore the anatomy. The fracture is corrected and set with either a plate or individual pins/screws by making an L-shaped incision above the heel.
Inside Midfoot (Navicular)
This frequent fracture splits the bone in half. A surgical incision is created over the fracture, and the two bones are straightened. Then they are held in place with screws or a plate and screws.
Outside Midfoot (Cuboid)
A compression injury that shortens the outer foot is what causes this particular fracture. Through direct bone-to-plate and screw insertion, cuboid surgery tries to stretch the foot’s outer. The plates and screws are removed when the fracture has fully healed.
Metatarsal Fracture
Doctors will treat some metatarsal fractures without surgery; however, for serious injuries, the doctor will recommend surgery. Surgery consists of an incision above the broken metatarsal bone and the surgeon will attach the broken ends with pins, screws, and plates to enable healing.
Toes (Phalanges)
Surgical intervention is not usually necessary to treat toe fractures. Doctors will recommend surgery to treat deformities brought on by displaced fractures. A pin is put through the toe’s tip after the toe is aligned, an incision is formed, and the fracture is secured with the help of the pin. Surgeons will remove the pin when the fracture has fully healed, which should take four to six weeks.
Non-Surgical Treatment of a Foot Fracture
The majority of the time, doctors can effectively treat a foot fracture without surgery, but only your doctor can determine this for sure given the nature and degree of your child’s fracture. To help your child heal as fast and securely as possible if no surgery is required, your doctor may advise some or all of the following measures.
Indulge, Ice, Compress, and Elevate
For a fractured foot or foot fracture, the advantages of applying rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) are widely known. Parents may minimize swelling and improve blood flow by keeping the injured foot off the ground, applying ice to it often during the day, wrapping it, and elevating it. The body’s natural healing process is accelerated by this initial therapy.
Lifting the injured body weight
Your child shouldn’t put any weight on the fractured foot for a considerable amount of time, as advised by your doctor. Even walking on a fractured foot can reinjure it and greatly lengthen the healing process.
Casts and hiking shoes
Your physician probably will provide you with advice on how to safeguard your child’s foot while it heals. The most common items are walking boots and casts. The degree and damage to the foot will determine how long your child should be immobile.
Foot Fracture Healing and Rehabilitation
Depending on the severity and particular kind of damage, most patients recuperating from a foot fracture will need to avoid putting any weight on the afflicted foot for six to twelve weeks or more. An effective mobility aid can speed your child’s recuperation and help you manage daily tasks during this period. A decent mobility aid is also crucial since it can aid your child in resisting the need to cheat when engaging in non-weight-bearing activities. Your child’s foot might easily re-injure itself after just one or two steps, which would prolong the rehabilitation. Recovery success or failure may depend on choosing the right mobility aid for your child’s injuries.
Conclusion
A child’s broken foot requires treatment by an orthopedic surgeon who understands the complex workings of the bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles of the foot or ankle. Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists with offices in Arlington, Dallas, Flower Mound, Frisco, and McKinney, TX are familiar with the latest surgical techniques for even the most difficult fractures to treat, including complex unhealed fractures. Our orthopedic specialists provide individualized treatment programs that cover every aspect of your care, including diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation, and aftercare. The type of fracture you have and the location of the injury will determine your course of therapy.
____________________
Footnote:
Call 214-556-0590 to make an appointment.
Comprehensive services for children from birth through adolescence at five convenient locations: Arlington, Dallas, Flower Mound, Frisco and McKinney.
