
HIP LABRAL TEAR
If your child needs surgery or casting, our Fracture Care Clinic opens every day and you do not need an appointment. Surgery rooms get scheduled every morning, so your child receives the care and attention they need right away.
Hip Labral Tear
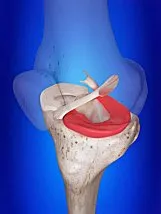 If you’ve ever had hip discomfort, you are aware of the pain and difficulty of walking. Playing sports or even just getting out of a chair is also painful. A torn labrum is a typical cause of hip discomfort, however, there are other possible reasons as well. One of the hip joint’s bones has a ring of strong tissue called the labrum. This tissue serves as both a stabilizer and a cushion. Hip instability and discomfort can result from a torn labrum. An additional risk factor for osteoarthritis of the hip, a painful and perhaps life-altering disease, is a ruptured labrum. Fortunately, there are nonsurgical and surgical methods for treating hip labral tears. With the right care, patients with torn labrums can effectively resume their regular activities.
If you’ve ever had hip discomfort, you are aware of the pain and difficulty of walking. Playing sports or even just getting out of a chair is also painful. A torn labrum is a typical cause of hip discomfort, however, there are other possible reasons as well. One of the hip joint’s bones has a ring of strong tissue called the labrum. This tissue serves as both a stabilizer and a cushion. Hip instability and discomfort can result from a torn labrum. An additional risk factor for osteoarthritis of the hip, a painful and perhaps life-altering disease, is a ruptured labrum. Fortunately, there are nonsurgical and surgical methods for treating hip labral tears. With the right care, patients with torn labrums can effectively resume their regular activities.
Surgeons can treat Labral rips surgically or with more conservative measures like physical therapy or injections. Arthroscopic and outpatient surgery are both options for treating labral tears. Surgeons can construct a new labrum if the labrum has been severely damaged and will not heal. The tight fibrocartilage ring that surrounds the acetabulum’s rim is known as the hip labrum (also known as the acetabular labrum). It creates a vacuum seal and stability between the bones by acting as a gasket between the acetabulum and the head of the femur. Additionally, it maintains the joint lubricated and full of fluid to ensure that the bones may move easily past one another. The labrum is crucial for dispersing stresses exerted on the hip joint and acting as a shock absorber.
Symptoms
Symptomless little labral rips are common. When they do appear in children, hip diseases like hip flexor or hip bursitis can cause similar symptoms.
- Pain, often toward the front of your child’s hip, not far from your groin, is one of them.
- Soreness that can go into your child’s knee or into your buttocks.
- Hip discomfort when turning it.
- A dull ache that worsens after engaging in physical activity, such as jogging, walking, or extended sitting.
- Immobility when moving your hip.
It’s significant to seek medical care if the pain is:
- intense
- getting worse
- Affecting your sports or regular activities
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
What causes a hip labral tear in children?
Hip labral tears in children can result from various factors, including:
-
- Sports and Physical Activities: Participation in high-impact sports, especially those that involve repetitive hip motion can increase the risk of hip labral tears.
- Hip Development Issues: Abnormalities in hip joint development, such as femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) or hip dysplasia, can predispose children to labral tears.
- Trauma: A sudden traumatic injury or fall, such as a direct blow to the hip, can lead to a labral tear.
- Overuse or Repetitive Stress: Repeated stress or overuse of the hip joint can contribute to labral tears over time.
How is a hip labral tear in a child diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis and treatment of a hip labral tear in children involve the following steps:
- Clinical Evaluation: A healthcare provider will assess the child’s medical history, symptoms, and conduct a physical examination to check for hip joint tenderness, range of motion, and hip stability.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or magnetic resonance arthrography (MRA) are commonly used to visualize the hip joint and confirm the presence and extent of the labral tear.
- Treatment Options: Treatment depends on the severity of the tear and the child’s symptoms:
- Conservative Management: In mild cases, non-surgical approaches may include rest, physical therapy to strengthen the hip muscles and improve joint stability, and anti-inflammatory medications to manage pain and inflammation.
- Hip Arthroscopy: For more severe tears, surgical intervention may be necessary. Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to repair or remove the torn labrum and address any underlying issues such as FAI.
- Rehabilitation: Following surgery, the child will require physical therapy and rehabilitation to regain hip joint strength, mobility, and function.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to assess the child’s progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
What are the potential long-term effects or complications of a hip labral tear in children?
The long-term effects and complications of a hip labral tear in children can vary but may include:
- Chronic Hip Pain: Without proper management, a labral tear can lead to persistent hip pain, a
- and potentially impact a child’s quality of life.
- Progressive Damage: An untreated labral tear can lead to damage to the hip joint, increasing the risk of hip osteoarthritis in adulthood.
- Functional Limitations: Severe tears or recurrent labral injuries may result in a decreased ability to participate in sports or physical activities.
- Surgical Risks: Surgical interventions, while often effective, come with potential risks and complications. Parents should discuss those risks with their healthcare provider.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment will prevent long-term complications and ensure the best possible outcomes for children with hip labral tears.
The doctors at Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists are highly skilled and experts at diagnosing and treating hip disorders.
Hip Labral Tear Causes
Anyone might experience a hip labral tear. Hip labrum tears can occur quickly or gradually as a result of hip trauma. Frequently stated reasons include hip overuse and repetitive hip movements (especially in certain sports and occupations).
- Fractures of the hip.
- Hip wear and tear over time.
- Labrum stress will increase with hip joint deformities including hip dysplasia and irregular bone structure that causes hip impingement.
- Osteoarthritis is one example of a degenerative disease. Hip labral tears and osteoarthritis are correlated in both directions:
- Labral tears will get worse if there is cartilage loss brought on by arthritis.
- A labral tear can increase your child’s risk of developing arthritis years down the road.
Diagnosis of a Hip Labral Tear
Due to the fact that many hip injuries have symptoms that are identical, doctors find labral tears challenging to diagnose. They are frequently misinterpreted as groin strains. A sports medicine physician at Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists or an orthopedist will conduct a physical examination and weigh your child’s symptoms before making a diagnosis. The Doctor will move your child’s hip in different ways to check whether your child feels any discomfort or clicking. The doctor will also take images of your child’s hip to further help with the diagnosis. Imaging methods include:
- An X-ray of your child’s hip can help detect structural issues and symptoms of arthritis.
- Electromagnetic fields are used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce photographs of your child’s body. It can assist a clinician in locating normal structures or hip-related soft tissue injuries, such as hip labral tears.
- In order to perform a magnetic resonance arthrogram (MRA), a medical expert must inject a dye into your child’s hip joint. A magnetic resonance arthrogram produces pictures that emphasize or contrast the hip cartilage and joint space in relation to the other bones.
Hip Labral Tear Treatment Options
How serious your child’s symptoms are will determine how your child is treated. Others require arthroscopic surgery to replace the torn piece of the labrum, while other people heal in a few weeks with conservative therapy like rest and limited activity. Hip labral tears can be treated in a variety of ways. Depending on the extent of the tear and your child’s discomfort, your doctor may often first advise nonsurgical treatment.
Nonsurgical Treatments
Doctors can treat hip labral rips without surgery if the symptoms are controlled and the labrum is kept from getting more harm:
- Reducing or stopping actions that hurt and make the injury worse is the goal of rest and activity adjustment. Your child’s symptoms can get better if your child quits doing the activities that caused the hip pain. When you continue these activities, though, the pain can come back if your child doesn’t receive more treatment.
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, such as naproxen sodium (Aleve) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, among others), help ease pain and lessen inflammation. Corticosteroid injections into the joint are another temporary method of pain management.
- If over-the-counter drugs don’t provide enough comfort, hip injections with anesthetics and steroids can assist momentarily in reducing pain and inflammation.
- Exercises used in physical therapy can help your child’s hip muscles become stronger and more flexible, enabling them to better support the joint and lessen the pain when he or she moves.
Surgery Treatments
Based on the circumstances, doctors will recommend open surgery, which necessitates a wider incision and usually includes a longer recovery period.
Arthroscopy
Your doctor could suggest surgery if the hip labral tear is severe or if the pain persists despite attempting nonsurgical alternatives. Arthroscopy is the procedure used most often to treat hip labral tears. The hip is accessed during this surgery by a surgeon who specializes in orthopedics through a number of tiny incisions. The surgeon finds the labral tear and uses surgical instruments to fix it with the use of a specialized camera. The camera refers to an arthroscope. Removing frayed labrum sections, sewing the tear back together, or replacing a missing portion of the labrum with tissue from another area of the body are all possible methods for treating a hip labral tear. Surgery can include side effects like infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and reoccurring problems if the repair doesn’t heal correctly. A return to sports generally takes 3-6 months.
Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO)
A periacetabular osteotomy (PAO) will repair your child’s labrum if hip dysplasia causes the condition. A surgeon will cut, carve and mold your child’s bones and realign them to their proper positions. Your child’s joint will suffer less additional injury as a result.
Surgical Dislocation and Osteochondroplasty
There are occasions when a surgeon needs to remove your child’s thigh bone from the joint. Your surgeon will delicately cut an incision on your child’s hip and this procedure will improve access for the next steps of the treatment, After that, your doctor can fix any labrum rips or other medical issues. Your surgeon will use screws to hold the bone back together once the issue has been fixed. This procedure is frequently utilized for larger abnormalities such as Perthes disease and slipping capital femoral epiphysis. In addition, it is used for other complicated issues requiring complete labral restoration (SCFE).
Hip Replacement (Arthroplasty)
Your child could require a total hip replacement if the joint deterioration appears severe. In this specific situation, your doctor will replace the natural ball and socket in your child’s joint with an artificial one. Your child should resume his or her regular activities in a few months, subject to the severity of the labral tear and the course of treatment. To stop your child’s symptoms from returning, parents should continue their child’s physical therapy and consult their doctor.
Recovery After Hip Labrum Repair
Since arthroscopic surgery is frequently performed as an outpatient treatment, your child can return home the same day. Your child can quickly resume low-impact exercises like walking after having his or her hip labrum repaired. Your surgeon will suggest that your child begin hip exercises with a physical therapist. This will help your child regain range of motion and strengthen the joint. After your child’s hip labral tear surgery, you might go back to work in one to two weeks if you have a profession that requires little physical activity, like an office job. If your employment places a lot of strain on your hip, you may either work with your physical therapists to identify a safe return date or speak with your employer about job changes that would allow you to gradually return to work while you recover.
Hip Labral Tear Outlook
A torn labrum might require up to 6 weeks for recovery. After two to six months, most competitive athletes may resume their sport. Your child will probably need crutches for 2 to 6 weeks following surgery if needed. According to research, labral tears seldom ever happen in people with normal bone structures. Your hip may be in danger of reinjury if structural variations in the hip are not treated. It’s crucial to consult a doctor if you think your child could have a labral tear. Conservative treatments may be sufficient to manage a minor tear. Larger rips could require surgery.
Why pick the Doctors at Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists
Due to the symptoms being identical to those of several other hip ailments, a ruptured labrum can be challenging to diagnose. And that’s the reason that parents should choose the doctors at Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists. Our doctors are experts in the management of hip conditions in Children. For the convenience of our patients, our offices are located in Arlington, Dallas, Flower Mound, Frisco, and McKinney, TX. We help children with all hip conditions because we have the greatest medical professionals and cutting-edge facilities. If your child is suffering from hip pain, please call the Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists as soon as you can and make an appointment for your child.
____________________
Footnote:
Call 214-556-0590 to make an appointment.
Comprehensive services for children from birth through adolescence at five convenient locations: Arlington, Dallas, Flower Mound, Frisco and McKinney.
