
TIBIA FRACTURES
Tibia fractures are the most common lower extremity fractures in children. They account for 10 to 15 percent of all pediatric fractures. Fractures can be described as low-energy — caused by twisting or falls from standing height.
If your child needs surgery or casting, our Fracture Care Clinic opens every day and you do not need an appointment. Surgery rooms get scheduled every morning, so your child receives the care and attention they need right away.
Tibia Fractures
Stress fractures are microscopic cracks in the bone. They are caused by repetitive force, often from overuse, such as jumping up and down repeatedly or running long distances. Stress fractures can also occur as a result of the normal use of a bone that has been weakened by a condition like osteoporosis. The weight-bearing bones of the lower leg and foot are the most susceptible to stress fractures. Track and field athletes and military recruits who carry heavy packs over long distances are most at risk, but stress fractures can happen to anyone. If your child begins playing a new sport, he or she may develop a stress fracture.
Tibia Stress Fracture Defined
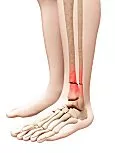 The lower leg is made up of two bones known as the tibia and fibula. The tibia is the larger and thicker of the two bones, and its function is load-bearing. The fibula is the thinner, smaller bone. Its primary function is to serve as a location for muscles to attach. Stress fractures can occur in either of these bones. The most common location, on the tibia bone, is two to three inches above the bony bit on the inside of the ankle (called medial malleolus). Long bones, such as the tibia, have an outer sheath that surrounds the periosteum, a hard-compact bone that contains bone marrow.
The lower leg is made up of two bones known as the tibia and fibula. The tibia is the larger and thicker of the two bones, and its function is load-bearing. The fibula is the thinner, smaller bone. Its primary function is to serve as a location for muscles to attach. Stress fractures can occur in either of these bones. The most common location, on the tibia bone, is two to three inches above the bony bit on the inside of the ankle (called medial malleolus). Long bones, such as the tibia, have an outer sheath that surrounds the periosteum, a hard-compact bone that contains bone marrow.
The tibia becomes overloaded as a result of continuous muscle contractions and impact stress forces. Fatigue, in particular, changes the distribution of forces in the bone. This is due to the muscles’ failure to absorb some of the load. As a result, the bone is under more strain. Many small impacts on the bone, no matter how minor, result in a cumulative build-up.
Causes of a Tibia Fracture
Repetitive stress or overtraining for sports is the most common cause of stress fractures of the tibia. It may also be linked to bone weakness caused by osteoporosis. Stress fractures are more common in women. Overuse is the most obvious cause of a tibial stress fracture; however, there are a number of other factors that can increase the risk of sustaining a tibial stress fracture:
Training
Sudden changes in a running surface, such as moving from grass to a lot of track or road running, can increase the chances of a stress fracture.
Foot Biomechanics
Overpronation or supination puts extra strain on the tibia bone. Overpronation and rolling in of the foot, flattening the arch, has the effect of rotating the shin bone inwards. As a result, the bone is subjected to increased torsion or twisting stresses.
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
How did my child fracture their tibia, and could it have been prevented?
Tibia fractures in children can result from various causes, such as falls, sports injuries, or accidents during play. Accidents happen with children, and it’s not always possible to prevent every injury. However, parents can take precautions by ensuring a safe environment, providing appropriate supervision, and encouraging the use of protective gear, especially during sports or high-impact activities.
How do doctors treat a child's fractured tibia, and will they need surgery?
The treatment approach for a fractured tibia depends on several factors, including the type and location of the fracture, the child’s age, and overall health. In some cases, a doctor will treat tibia fracture non-surgically with casting or bracing to allow the bones to heal naturally. In more complex or displaced fractures, doctors will perform surgery to realign and stabilize the bones. The doctor will assess the specific details of the fracture and provide a personalized treatment plan.
How long does it take for a tibia fracture to heal, and a tibia fracture cause any long-term effects on my child's leg?
The Doctors at Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists are experts in treating children and adolescents for a Tibia Fracture. See the Specialists for children.
Tibia Fracture Symptoms
Tibial stress fracture symptoms include those that are similar to shin splints (medial tibial stress syndrome):
- Pain on the inside of the shin, usually in the lower third of the shin.
- Symptoms frequently appear after long-distance running.
- When you press upon that area, your child’s leg will feel tender and sore.
- Swelling around the fracture site.
- If your child has a stress fracture, you may notice a particularly tender spot at the stress fracture’s exact location.
Diagnosis of a Tibia Fracture
Before conducting a physical examination, your doctor will go over your child’s medical history and symptoms. The doctor will also examine the leg and order X-rays and possibly other scans to help with the diagnosis:
- X-rays: High electromagnetic energy beams make an image of the broken bones. When the X-ray does not disclose a fracture, the doctor must consider a stress fractures and additional tests.
- Bone scan: This refers to an imaging technique that involves injecting a radioactive drug into the bone to detect any damage or disease.
- CT scan: Using X-rays from various angles, detailed images of the tibia are obtained.
- MRI Scan: An imaging study that produces detailed images of the tibia by using a large magnetic field and radio waves.
Tibia Stress Fracture Treatment
All physical activity must stop during stress fracture treatment. Crutches or even a walking boot may be used to relieve tibial stress, particularly during daily activities such as walking. X-rays, MRIs, or a bone scan may help determine the extent of the stress fracture. Depending on the severity of the stress fracture, a full recovery can occur. Once completely symptom-free, a gradual return to sports and activity is recommended. If rest and conservative treatment do not appear to work, helping, aggressive measures such as surgical intervention may be considered.
Rest
Your child should rest for 8 weeks if you suspect and the doctor diagnoses a stress fracture. All running and weight-bearing activities should be avoided. This allows your child’s injury to start healing. If pain-free, substitute swimming or cycling or use the opportunity to work on upper-body strength in the gym. Running in the water with a buoyancy aid or belt is also an excellent substitute for road running. A doctor will examine the leg and decide when it is safe to return to training. Stress fractures do not appear on an x-ray at first. However, after 2 or 3 weeks, you may notice some signs. As a result, it is critical to perform another x-ray after a period of rest.
Taping
A simple shin-taping technique can help reduce shin strain. It works by supporting and pulling the muscles of the lower leg toward the bone. As a result, the rotation of the tibia is reduced. However, if your child has a suspected tibial stress fracture, your child should not be running and playing.
Exercises
When returning to weight-bearing exercise, it is especially important to stretch and strengthen the muscles at the back of the lower leg. They may be tight and in poor condition after a period of rest. This increases the likelihood of suffering additional shin pain as a result of medial tibial stress syndrome (shin splints).
Training errors
Analyze your child’s activities to see if or how they contributed to your child’s injury. Do you need to replace your child’s shoes? Running shoes last about 500 miles or 6 months before needing to be replaced.
Foot biomechanics
Gait analysis to detect any biomechanical issues with the foot that may have heightened the risk of injury. Foot problems such as overpronation can be resolved with orthotic inserts worn in shoes.
Massage
Massage Sports massage for the calf muscles at the back of the lower leg can relax them, releasing any muscle spasms, tight knots, lumps, or bumps, making them more efficient at absorbing running forces when normal training resumes. If these methods prove ineffective, your doctor will advise you to use:
Splints
Made of plastic and fiberglass, splints are used to immobilize the joint.
Casting
This is a protective shell made of fiber or plaster that has been molded to protect the broken bones.
Braces are made of plaster or fiber and serve as a protective shield to align the damaged bone. The recovery time from a tibial stress fracture depends on the severity of the fracture. A person will usually recover in 4 to 6 months. Recovery time for a complete break may be longer than for a partial break, and it may take longer if a person is in poor health for other reasons. It may take longer than this time frame for a person to resume normal activities. Following a leg fracture, people should always follow their doctor’s recommendations for returning to walking, exercising, and other physical activity. Exercises that strengthen the hips, calves, and thighs, for example, can help to relieve pressure on the tibia bone. This protection may also help to prevent future injuries.
Risk Factor for Breaking a Tibia
Specific sports
Stress fractures are much more common in athletes who compete in high-impact sports including gymnastics, basketball, tennis, dance, and athletics.
Enhanced activity
People who abruptly go from a sedentary lifestyle to an active training program or who quickly increase the intensity, duration, or frequency of training sessions are more likely to get stress fractures.
Foot problems
Stress fractures are more common in people who have flat feet or high, rigid arches. Worn footwear adds to the problem.
Bone weakening
Osteoporosis, for example, can weaken bones and make stress fractures more likely.
Prior stress fractures
Your child is more prone to have further stress fractures if he or she has already had one or more.
How Medical City Children’s Orthopedic and Spine Specialists Care For Tibia Fractures
The board-certified pediatric orthopedic surgeons and fellowship-trained physicians at Medical City Children’s Orthopedic and Spine Specialists treat children, adolescents, and young adults who have fractures of all complexities. Our expertise gives room for the accurate diagnosis of problems that relate to the growing musculoskeletal system. We will develop optimal care plans that will ensure that your child’s specific condition is catered for.
Finally, we offer personalized treatment and urgent pediatric care services at all of our four locations — Arlington, Dallas, Flower Mound, Frisco, and McKinney, TX. If you notice any symptoms of a stress fracture in your child, don’t hesitate to contact us to avoid complications.
____________________
Footnote:
Call 214-556-0590 to make an appointment.

