
Avulsion Fractures
Avulsion fractures usually occur in young athletes. They may sprint, punch, slide, or engage in other movements that involve jerky movements or sharp turns. A piece of bone attached to a ligament or tendon separates from the body of the bone. It may take up to 12 weeks to fully heal.
If your child needs surgery or casting, our Fracture Care Clinic opens every day and you do not need an appointment. Surgery rooms get scheduled every morning, so your child receives the care and attention they need right away.
Are Avulsion Fractures Serious?
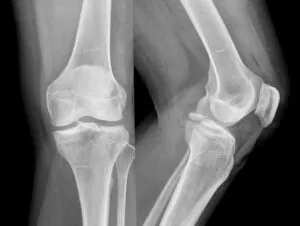 You may wonder if an injury is serious enough to warrant an emergency room visit. Any fracture is serious, including if you think your child has broken a bone; so first go to the emergency room and have your child diagnosed and treated. Then come see us. We are pediatric specialists who will ensure your child heals properly and returns to his or her daily routine of having fun.
You may wonder if an injury is serious enough to warrant an emergency room visit. Any fracture is serious, including if you think your child has broken a bone; so first go to the emergency room and have your child diagnosed and treated. Then come see us. We are pediatric specialists who will ensure your child heals properly and returns to his or her daily routine of having fun.
Types of Avulsion Fractures
- Pelvic avulsion fracture
- Fibular avulsion fracture
- Medial epicondyle avulsion fracture
- Finger avulsion fracture
Causes
An abrupt, strong tug on a tendon while the bone is moving in the opposite direction frequently results in an avulsion fracture. A fifth metatarsal injury, which affects the bone on the outside of the midfoot, serves as an illustration. This bone’s base is where the peroneal tendon connects. When the foot is twisted, the peroneal tendon frequently contracts firmly, pulling the foot obliquely in the opposite direction from the twisting force. Where the tendon joins to the bone, this results in a break in the bone. The good news is that with only rest and patience, these fractures typically heal quickly.
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
What causes Avulsion Fractures?
Avulsion fractures are typically caused by a sudden and forceful contraction of a muscle or a strong pull from a ligament. This can occur during activities such as jumping, sprinting, or sudden stops. They are common in sports that involve explosive movements or quick changes in direction, such as soccer, basketball, and gymnastics.
How are Avulsion Fractures Diagnosed and Treated
Diagnosis is usually made through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans. Treatment depends on the severity of the fracture, but common approaches include:
- Rest and Immobilization: Mild avulsion fractures may heal with rest and the use of a brace or cast to immobilize the affected area.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises help restore strength and flexibility as the fracture heals.
- Surgery: In some cases, especially when bone fragments are displaced significantly or the fracture involves a weight-bearing joint, surgery may be necessary to reattach the bone fragment.
What is the recovery time for an Avulsion Fracture?
The recovery time for avulsion fractures varies based on factors such as the location and severity of the fracture, the individual’s age and overall health, and the chosen treatment approach. Mild avulsion fractures may heal within a few weeks with rest and conservative treatment. More complex fractures or those requiring surgery may take several months to heal completely. Physical therapy is often an essential part of the recovery process to regain strength, flexibility, and functionality.
At Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists, we treat children with Avulsion Fractures
What Is the Diagnosis of an Avulsion Fracture?
A physical examination of the affected region, a review of the patient’s medical history, and imaging studies, such as:
- X-rays
- CT scan for computerized tomography
- MRI scan for magnetic resonance imaging
- Ultrasound
Who is Affected by Avulsion Fractures?
Avulsion fractures are common in children who play sports that include skiers, ballet dancers, football players, and gymnasts. They may do several abrupt turns, leaps, and kicks during their activities. Avulsion fractures, on the other hand, can happen to anybody and cause sprain-like injuries like a twisted ankle. Avulsion fractures hurt, and missing out on favorite sports or other cherished activities might hurt children much more.
Who Needs Surgery for an Avulsion Fracture?
Surgery is typically not necessary for avulsion fractures. But let’s say your child suffers an injury where the bone linked to the tendon or ligament is located more than 2 cm from the primary bone. The doctor will conduct one of the following two procedures:
Open Reduction
After cutting the body, the surgeon realigns the bones.
Internal Fixation
To permanently realign bones, the surgeon adds metal hardware. Pins, plates, screws, and rods are a few examples of hardware. During the procedure, your child may fall asleep. Our physician will use the most effective technique, such as a general anesthetic or localized anesthetic like an epidural. Your child won’t experience anything in either scenario.
What is the Recovery Time for Avulsion Fractures?
For a few weeks, your child might have to use a cast or splint. The normal healing time for fractures is three to twelve weeks. A brief period of rest followed by crutches is beneficial for an avulsion fracture in the pelvis or anywhere else where our doctor cannot put a cast. After a few weeks, the doctor can let your child apply weight and restart as tolerated in sporting activities. Ask your doctor when your child may resume his or her sports activities. If your child returns too soon, the child can get hurt once again.
Do I Need to See an Expert for Further Information?
After receiving care at the emergency room, you should visit one of our expert orthopedists. Your child’s skeletal and muscular systems are the focus of orthopedics. You might have to see our doctor as frequently as twice each week, depending on your child’s injury. Our orthopedist will ensure a rapid recovery and request more X-rays as necessary.
Treatment
Depending on which bone your child has injured, several treatments are available for avulsion fractures.
Treatment for an Ankle Avulsion Fracture
Rest and ice are the primary therapies for an ankle avulsion fracture. As the ankle heals, the child should avoid putting any weight on it and take steps to prevent swelling by elevating the ankle and using ice. Use an ice pack or ice wrapped in a towel to treat an injury. By taking these precautions and applying ice to the wound, parents can stop the bone from suffering more damage. To keep the ankle stable, your doctor could apply a cast or boot. Until the ankle has recovered, your child will need to wear the boot or cast and may need to use crutches to go around to prevent placing weight on the injured ankle. Physical therapy might assist your child in regaining ankle mobility once the fracture has healed. A physical therapist will demonstrate to you how to carry out bone-strengthening and range-of-motion-improving exercises. Your child could require surgery to correct the alignment and anatomy of the bone if it has been too severely misaligned. You can ask your doctor if surgery is required.
Treatment for a Finger Avulsion Fracture
When an item, such as a ball, strikes the tip of your finger and causes it to bend downward, your finger may break. Doctors use the term “baseball finger” or “mallet finger” to describe this sort of damage. The damage may cause the finger’s tendon to peel away from the bone. Another sort of injury, known as “jersey finger,” is frequent in sports like football and rugby. When a player grabs another player’s jersey, their finger is trapped and pulled, resulting in a “jersey finger.” The tendon pulls away from the bone as a result of this motion. A finger avulsion fracture requires a slightly more complicated treatment than typical bone fractures. In order to prevent further damage to the finger, doctors will stabilize the finger. To make sure your child receives the proper care, our doctors specialize in children and specialize in hands.
For a few weeks, your child will probably need to keep the injured finger straight with a splint while it heals. Physical therapy can help restore mobility and functionality in the finger once it has healed. In some cases, surgery will be conducted to treat a wounded finger. During surgery, a surgeon will place pins in the bone to keep the broken bone fragments together as they heal. It could also need sewing a ripped tendon back together, depending on the kind of damage.
Treatment for a Hip Avulsion Fracture
Rest is the main course of action for pelvic or hip avulsion fractures. To prevent further damage to the hip while it heals, your child’s doctor may advise using crutches. In addition, the doctor will recommend that ice be used for 20 minutes at a time for the first several days following the accident. Your doctor will recommend a physical therapist for assistance in strengthening and stretching your child’s hip once the fracture has mostly healed. Surgery might be needed to repair the bone if it has moved far from its original position. To maintain the hip in place as it heals, surgeons may employ metal pins or screws.
Will my Child be Asleep During Surgery?
During the procedure, your child will be asleep. Your physician will use the most effective technique, such as a general anesthetic or localized anesthetic like an epidural. Your child won’t experience anything in either scenario.
How can I Lower my Child’s Chance of Suffering an Avulsion Fracture?
Avulsion fractures are difficult to avoid, although it is feasible to lower the risk. Children playing sports can lower their risk of an avulsion fracture by doing the following:
- Before practicing or playing a game, spend five to ten minutes warming up.
- Avoid pushing your child to complete a task that may be too challenging.
- Your child should be able to avoid any injuries by exercising caution.
Summary
A fragment of bone that rips away from the surrounding bone results in an avulsion fracture. Depending on the degree of bone displacement, certain avulsion fractures are simple to identify and diagnose. Since the soft tissue maintains the bone in place in some cases and the bone separation is not as obvious, it might be challenging to detect certain conditions. Based on the location and seriousness of the injury, your doctor will decide how to treat your child. Although immobilization is a common treatment for many minor avulsion fractures, in some severe cases doctors will conduct surgery. Before children return to sports or other activities following an avulsion fracture, parents should consult with our specialists.
Why Choose Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists
Orthopedics is a specialty of our doctors and surgeons at Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists. They understand your concerns, can answer your questions regarding your child’s condition, and know how to use their specialized knowledge and training to find a medical solution. Richard Hostin, MD, Shyam Kishan, MD, and Kathryn Wiesman, MD, specialize in children and are considered to be the very best by many children’s doctors.
The following are just a few of the many reasons why patients might choose Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists.
- Expertise in the spine: The team of specialists are spine experts. They specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of spinal conditions, ensuring the best possible care for their patients.
- Cutting-edge technology: Our practice uses the latest technology and techniques to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions. In addition, we use minimally invasive procedures that reduce pain and promote faster recovery.
- Comprehensive care: Our practice offers a full range of services, from diagnostic imaging and physical therapy to surgery. We ensure that patients receive complete, seamless care for their spinal conditions.
- Dedicated facilities: Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists is dedicated to providing patients with a safe and comfortable environment.
Finally, our board-certified physicians and fellowship-trained orthopedic surgeons use the full range of treatments to treat their patients. Medical City Children’s Orthopedics and Spine Specialists are experts with offices in Arlington, Dallas, Flower Mound, Frisco, and McKinney, TX, and offer cutting-edge technology, comprehensive care, and dedicated facilities to ensure the best possible care for their patients. Call today to make an appointment for your child.
____________________
Footnote:
Call 214-556-0590 to make an appointment.
Comprehensive services for children from birth through adolescence at five convenient locations: Arlington, Dallas, Flower Mound, Frisco and McKinney.
